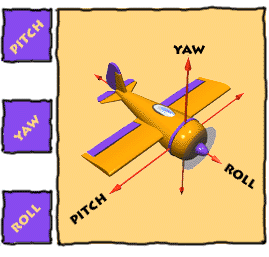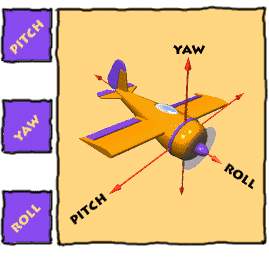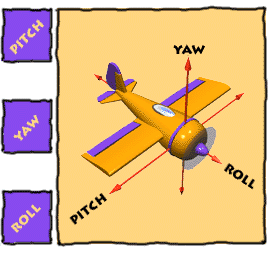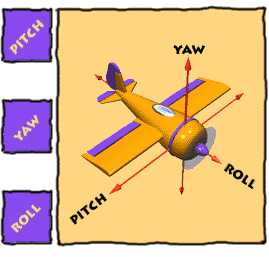
[ YAW PITCH ROLL ]
3D좌표 X, Y, Z 3개의 축을 기준으로 회전하는 방향에 따라 3가지로 구분할 수 있습니다.
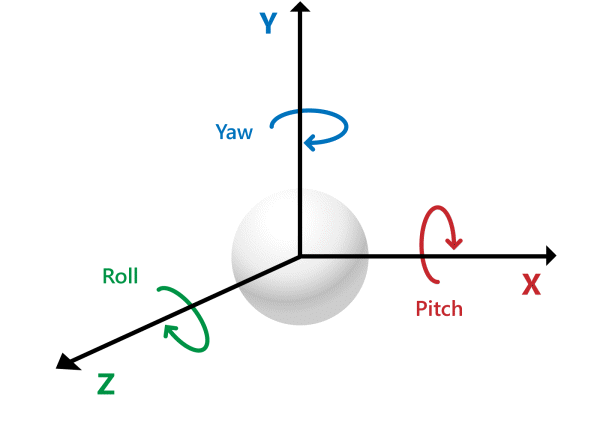
Y축 회전 : Yawing ( 요 )
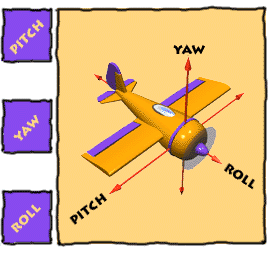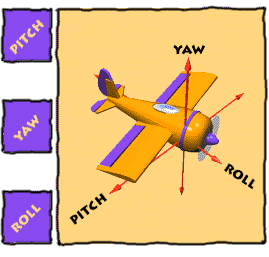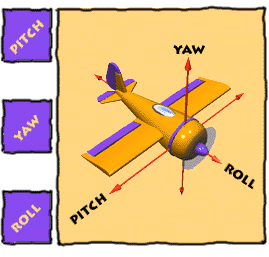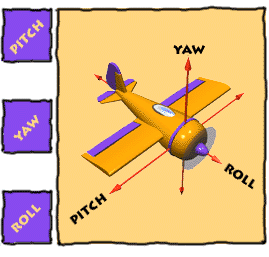
X 축 회전 : Pitching ( 피치 )
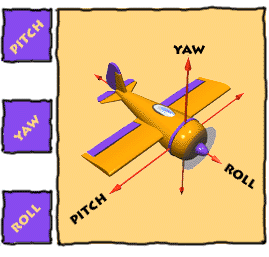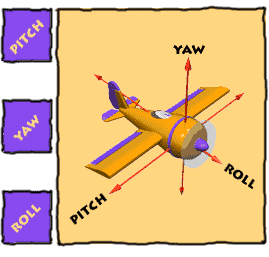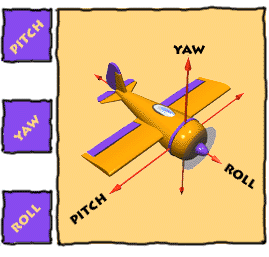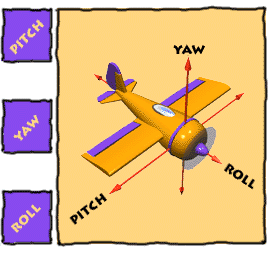
Z 축 회전 : Rolling ( 롤 )
[ 짐벌락 ( Gimbal Lock ) ]
X,Y,Z 축을 이용한 요피치롤을 알고난 뒤 다음으로 알아볼 내용은 짐벌락(Gimbal Lock) 입니다.
우선 간단한 이미지를 통하여 짐벌락 회전방식에 대하여 알아보도록 합니다.
우선 짐벌이란 단일축하나를 중심으로 물체가 회전하도록 만들어진 구조입니다.
제일 외부 축은 요(Yaw)
중앙 축은 피치(Pitch)
가장 안쪽의 축은 롤(Roll)
즉, 가장 외부의 요의 회전은 피치와 롤에 영향을 줍니다.
피치의 회전은 롤에 영향을 주게되는 형식 입니다.
이런 구조는 고리가 종속 관계를 형성합니다.
종속 관계로 인하여 의도치않게 두개이상의 고리가 겹치면 겹친 고리는 함께움직이게 되며 한 축의 회전각이 소실되는 현상이있습니다. 이것이 바로 "짐벌락 현상" 이라고 합니다.
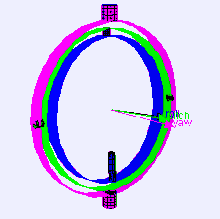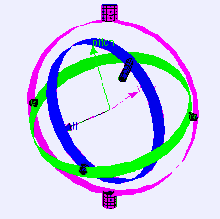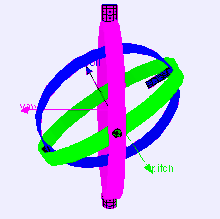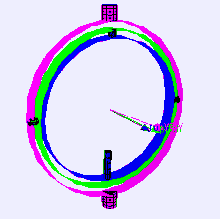
짐벌락 현상의 이해는 아래의 이미지를 참고 합니다.
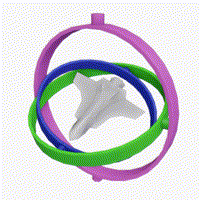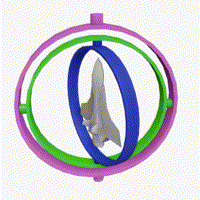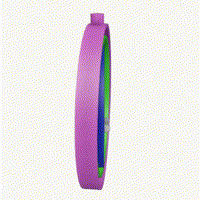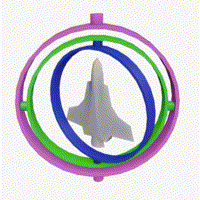
이미지에서 초록(피치)고리가 회전하다 보라(요)고리와 합쳐지며 함께 회전하는 모습을 볼 수 있습니다.
이런 경우 2개의 고리는 각각의 기능을 실행하지못하며 하나의 움직임이 되어버립니다.
이렇게 X,Y,Z 축이 종속적인 관계를 가지는 이유는 "오일러 각"을 계산하는 방법에 원인이 있습니다.
"오일러 각"은 회전을 세번에 나눠서 순차적으로 계산하기 때문입니다.
오일러 각(Euler Angle)
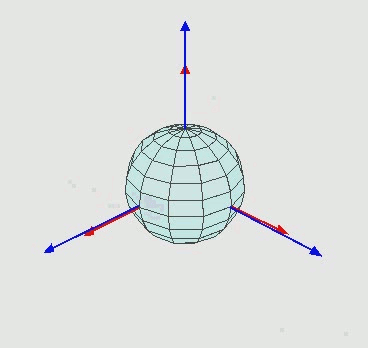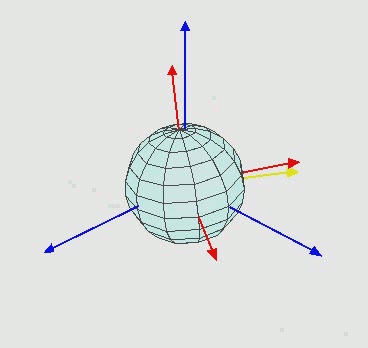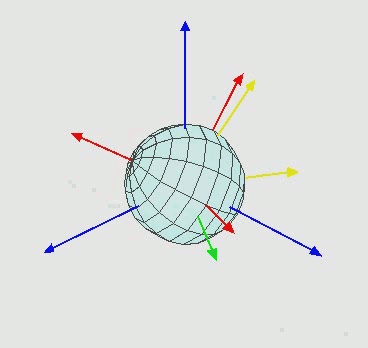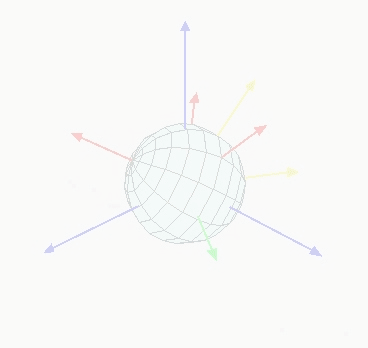
1) A의 오브젝트를 X축에대하여 회전하여 A'의 방향을 가지게 된다고 할때
2) 이후 Y축에대하여 회전하면 A' 에대한 회전으로 A''의 결과가 나오게 됩니다.
3) 이후 Z축에대하여 회전하면 A'' 에대한 회전으로 A'''의 결과를 최종적으로 가지고 오는데
A', A'', A''' 는 각각 독립적이지않으며 A', A''는 과정 A'''의 결과를 가져오기 때문입니다.
위의 계산과정에서 이전 언급한 두개의 축이상이 겹쳐 각각의 축의 의미가 소실되는
짐벌락현상(GimbalLock)은 쿼터니언(Quaternion)을 통하여 해결이 가능합니다.
(짐벌락현상은 오일러각을 사용하는이상 종속순서를 바꾸더라도 해결되지 않습니다.)
짐벌락 현상 영상 참조!
[ 쿼터니언( Quaternion ) / 사원수 ]
위에서언급한 짐벌락현상을 해결하기위한 방법입니다.
기존의 회전행렬에 회전각 하나를 추가하여 그축을 기준으로 회전 행렬을 구하는 방식 입니다.




쿼터니언의 장점 & 단점
장점
- 일반 회전행렬에 비해 계산량이 적습니다.
- 메모리를 적게 사용합니다.
- 가장 중요한 장점은 짐벌락 현상을 해결합니다.
단점
- 직관적으로 이해하기가 어렵습니다
3D 회전축인 x, y, z의 회전축을 가지고있으며 w의 회전값(radian)을 가지고 있습니다.
회전 방향은 CCW 입니다.
VS D3D 내에서 Quaternion 참조
// Util.h
Vector3 QuaternionToYawPtichRoll(Quaternion q1);
// Util.cpp
Vector3 Util::QuaternionToYawPtichRoll(Quaternion q1)
{
float sqw = q1.w * q1.w;
float sqx = q1.x * q1.x;
float sqy = q1.y * q1.y;
float sqz = q1.z * q1.z;
float unit = sqx + sqy + sqz + sqw; // if normalised is one, otherwise is correction factor
float test = q1.x * q1.w - q1.y * q1.z;
Vector3 v;
if (test > 0.4995f * unit) { // singularity at north pole
v.y = 2.0f * atan2f(q1.y, q1.x);
v.x = PI / 2.0f;
v.z = 0;
return NormalizeAngles(v);
}
if (test < -0.4995f * unit) { // singularity at south pole
v.y = -2.0f * atan2f(q1.y, q1.x);
v.x = -PI / 2.0f;
v.z = 0;
return NormalizeAngles(v);
}
Quaternion q = Quaternion(q1.w, q1.z, q1.x, q1.y);
// Yaw
v.y = atan2f(2.0f * q.x * q.w + 2.0f * q.y * q.z, 1.0f - 2.0f * (q.z * q.z + q.w * q.w));
// Pitch
v.x = asinf(2.0f * (q.x * q.z - q.w * q.y));
// Roll
v.z = atan2f(2.0f * q.x * q.y + 2.0f * q.z * q.w, 1.0f - 2.0f * (q.y * q.y + q.z * q.z));
return NormalizeAngles(v);
}// SimpleMath.h Line 659 ~ 725
// Quaternion
struct Quaternion : public XMFLOAT4
{
Quaternion() noexcept : XMFLOAT4(0, 0, 0, 1.f) {}
constexpr Quaternion(float ix, float iy, float iz, float iw) noexcept : XMFLOAT4(ix, iy, iz, iw) {}
Quaternion(const Vector3& v, float scalar) noexcept : XMFLOAT4(v.x, v.y, v.z, scalar) {}
explicit Quaternion(const Vector4& v) noexcept : XMFLOAT4(v.x, v.y, v.z, v.w) {}
explicit Quaternion(_In_reads_(4) const float *pArray) noexcept : XMFLOAT4(pArray) {}
Quaternion(FXMVECTOR V) noexcept { XMStoreFloat4(this, V); }
Quaternion(const XMFLOAT4& q) noexcept { this->x = q.x; this->y = q.y; this->z = q.z; this->w = q.w; }
explicit Quaternion(const XMVECTORF32& F) noexcept { this->x = F.f[0]; this->y = F.f[1]; this->z = F.f[2]; this->w = F.f[3]; }
Quaternion(const Quaternion&) = default;
Quaternion& operator=(const Quaternion&) = default;
Quaternion(Quaternion&&) = default;
Quaternion& operator=(Quaternion&&) = default;
operator XMVECTOR() const noexcept { return XMLoadFloat4(this); }
// Comparison operators
bool operator == (const Quaternion& q) const noexcept;
bool operator != (const Quaternion& q) const noexcept;
// Assignment operators
Quaternion& operator= (const XMVECTORF32& F) noexcept { x = F.f[0]; y = F.f[1]; z = F.f[2]; w = F.f[3]; return *this; }
Quaternion& operator+= (const Quaternion& q) noexcept;
Quaternion& operator-= (const Quaternion& q) noexcept;
Quaternion& operator*= (const Quaternion& q) noexcept;
Quaternion& operator*= (float S) noexcept;
Quaternion& operator/= (const Quaternion& q) noexcept;
// Unary operators
Quaternion operator+ () const noexcept { return *this; }
Quaternion operator- () const noexcept;
// Quaternion operations
float Length() const noexcept;
float LengthSquared() const noexcept;
void Normalize() noexcept;
void Normalize(Quaternion& result) const noexcept;
void Conjugate() noexcept;
void Conjugate(Quaternion& result) const noexcept;
void Inverse(Quaternion& result) const noexcept;
float Dot(const Quaternion& Q) const noexcept;
// Static functions
static Quaternion CreateFromAxisAngle(const Vector3& axis, float angle) noexcept;
static Quaternion CreateFromYawPitchRoll(float yaw, float pitch, float roll) noexcept;
static Quaternion CreateFromRotationMatrix(const Matrix& M) noexcept;
static void Lerp(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2, float t, Quaternion& result) noexcept;
static Quaternion Lerp(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2, float t) noexcept;
static void Slerp(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2, float t, Quaternion& result) noexcept;
static Quaternion Slerp(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2, float t) noexcept;
static void Concatenate(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2, Quaternion& result) noexcept;
static Quaternion Concatenate(const Quaternion& q1, const Quaternion& q2) noexcept;
// Constants
static const Quaternion Identity;
};'공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++/DX11] 3D 가위바위보 (1) | 2023.05.21 |
|---|---|
| [C++/DX11] 리소스매니저클래스, XML파일 저장&불러오기 (0) | 2023.05.18 |
| [C++] 상속 접근 지정자 (Inheritance And Access Specifier) (0) | 2023.05.14 |
| [C++] 특수 멤버 함수 (Special Member Function) (0) | 2023.05.14 |
| [자료구조] 객체 관계 (Object Relationship) (0) | 2023.05.13 |


댓글